How to Be Fit with Pure Vegetarian Diet

Nowadays, people have become much more conscious about their health due to increasing health awareness programs. Consumers have drastically changed their food habits in due course of decades. They are relying on healthier food products and moving towards functional food products such as green tea, chyawanprash, a different category of probiotic products, etc.
For a few decades, significant consumers have changed their food habits towards animal products (meat, poultry, fish, egg) in search of high-quality proteins for building their muscles. It was my personal experience noted during a marriage ceremony program that around 70% or 3/4th of the population were there on the meat/animal product side while the remaining 1/3rd population was there on the vegetable or plant-based food side.
It is a well-established food fact that in comparison to plant proteins, animal proteins are good quality proteins with greater bioavailability and high PER value (Protein Efficiency Ratio). Beyond supplying good quality proteins, animal food products contain a significant fraction of saturated fat which may put the person at a high risk of non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), respiratory distress syndrome, colon cancer, type 2 diabetes mellitus, etc.
Due to increasing noncommunicable diseases, people are again moving towards plant-based food products to rejuvenate their health.
But, it’s a great challenge for the pure vegetarian population to fulfill their protein requirement with plant-based food materials. In this article, an effort has been put to summarize the “Fitness Formula” with vegetables and other plant-based food materials.
Before discussing the important aspects of a vegetarian diet, we, first have to understand, why it is in demand in today’s context. Why, are people, everywhere advocating following a vegetarian diet over an animal-based food routine?
To understand, its importance, let’s go through some statistical data revealing the health implications of an animal-based diet system or food rich in saturated fat and a sedentary lifestyle.
What are the Current Public Health Issues Globally?
Around the world, the lifestyle of people has changed from highly Active to moderately active and towards sedentary at the end. Which is causing a variety of Non-communicable diseases such as Cardiovascular diseases, type 2 Diabetes mellitus, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in females, Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Colon cancer, and several other overweight and obesity-linked diseases.
Global Non-communicable Facts by World Health Organization (as of 2022)
- Around 41 million people are killed each year by Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) which is equivalent to 74% of all deaths globally.
- Around 17 million people are killed each year by NCDs before attaining the age of 70 and approximately 86% of deaths are premature deaths belonging to low and middle socio-economic countries.
- Around 77% of all NCDs deaths belong to low and middle-income countries.
- Out of total NCDs deaths, 17.9 million deaths were due to cardiovascular diseases followed by 9.3 million due to cancer, 4.1 million due to chronic respiratory diseases, and around 2 million deaths due to diabetes including associated kidney problems, taken place.
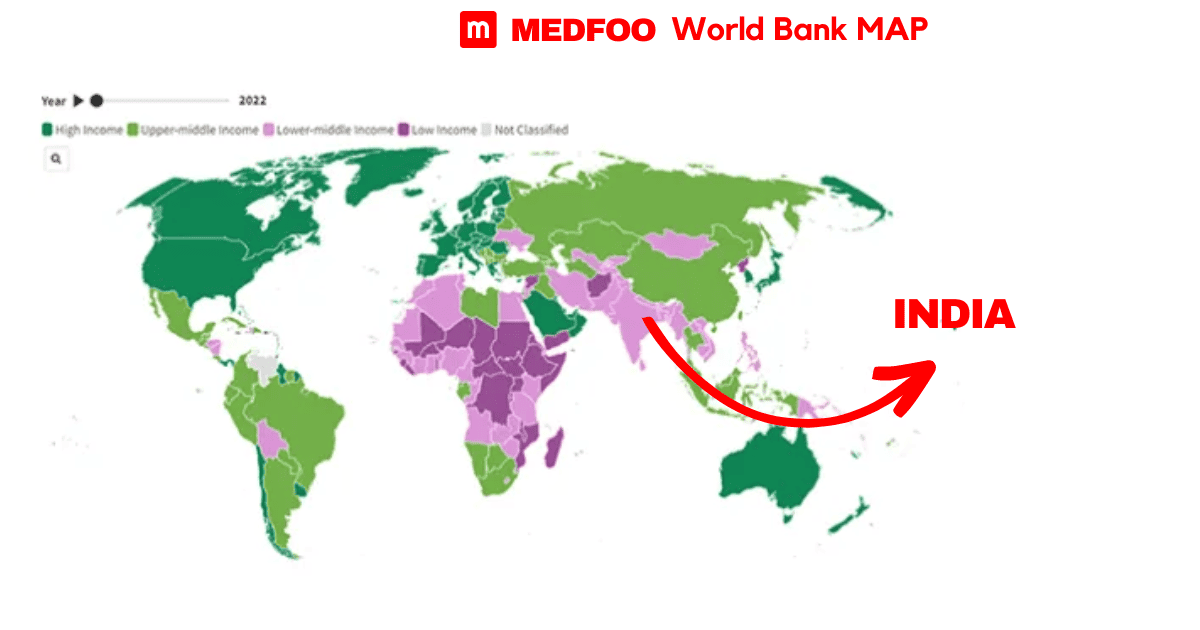
India comes under the category of low-middle income countries as per World Bank statistics, 2023. So, India is one of the countries where 86% of total NCDs death are taken place. It is the most critical and alarming issue which must be addressed at National and International levels so as to reduce the frequency of NCDs in Low-middle socio-economic countries.
But, interestingly, People, nowadays, become much more conscious about their health, and that’s why the pursuit of fitness is a goal shared by many individuals around the world. While there are various dietary approaches to support fitness goals, following a pure vegetarian diet can provide an excellent foundation for achieving optimal health and physical well-being. Contrary to popular belief, a vegetarian diet can offer all the necessary nutrients required for fitness, including protein, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. In this article, we will explore how to achieve fitness while following a purely vegetarian diet.
- Plant-Based Protein Sources
Protein is a crucial macronutrient for building and repairing muscles. While animal products are common sources of protein, there are numerous plant-based alternatives available for vegetarians. Incorporate protein-rich foods such as legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), tofu, tempeh, seitan, quinoa, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and nuts into your diet. Combining different plant-based protein sources can help ensure you receive a complete amino acid profile.

- Whole Grains and Complex Carbohydrates
Whole grains provide a steady release of energy and are an essential component of a vegetarian diet for fitness. Incorporate whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, and whole wheat bread into your meals. These complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy for workouts and aid in muscle recovery.

- Nutrient-Dense Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are vital for maintaining overall health and fitness. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that support the optimal functioning of the body. Include a wide variety of colorful fruits and vegetables in your diet, such as leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower), and sweet potatoes. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential micronutrients while promoting overall well-being.
- Healthy Fat Source
Fat is an important macromolecule needed for balanced metabolic health. Out of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, the unsaturated fatty acids are the healthy fat that helps in maintaining good cholesterol levels, triglyceride, HDL, and LDL levels. Healthy fats are an important part of a balanced diet for fitness. Interestingly, plant fat is rich in unsaturated fatty acids which are good for health such as olive oil, canola oil, mustard oil, linseed oil, flax seed oil, etc. For a healthy lifestyle, replace animal fat with plant-based fats in your diet such as avocados, nuts, seeds (flaxseeds, chia seeds), and olive oil into your meals. This does not mean that one should not take saturated fat but in a very little amount because it helps in the synthesis of hormones, and nutrient absorption, and also provides calories.
Globally, people are changing their lifestyle from active to sedentary that’s why the consumption of animal fat may be lethal because people have now moderate to low physical activity to burn the fat. Resultingly, it gets collected deep in the arteries and causes a variety of cardiac problems.

- Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for fitness and overall health. Water is essential for optimal bodily functions, including digestion, metabolism, and muscle recovery. Ensure you drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day and during workouts. Herbal teas and fresh fruit juices can also contribute to your hydration needs.
- Meal Planning and Preparation
Effective meal planning and preparation are key to maintaining a healthy vegetarian diet for fitness. Plan your meals in advance to ensure they include a balance of macronutrients and micronutrients. Prepare your meals at home, using fresh ingredients, to have better control over portion sizes and nutrient content. This practice can also help you avoid relying on processed vegetarian convenience foods, which may be high in sodium, unhealthy fats, and additives.

- Supplementation, if necessary
While a well-balanced vegetarian diet can meet most nutritional needs, some individuals may benefit from specific supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to assess if you require supplementation, particularly for nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, zinc, or omega-3 fatty acids.

- Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition
To optimize your workouts and support muscle recovery, pay attention to your pre-and post-workout nutrition. Before exercising, consume a balanced meal or snack that includes carbohydrates for energy and a small amount of protein to prepare your muscles. Examples of pre-workout vegetarian options could be a banana with almond butter, a protein smoothie with plant-based protein powder, or a bowl of oatmeal with berries.
After your workout, prioritize replenishing your body with nutrients to aid in muscle repair and recovery. Consume a combination of carbohydrates and protein within 30 minutes to an hour after exercising. This could be a post-workout smoothie made with plant-based protein, fruits, and leafy greens, or a balanced meal containing whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.

- Monitoring Nutrient Intake
While a pure vegetarian diet can provide all the necessary nutrients for fitness, it’s essential to monitor your nutrient intake, especially if you have specific dietary restrictions or preferences. Keep track of your macronutrient (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) and micronutrient (vitamins and minerals) intake to ensure you’re meeting your body’s requirements. There are various apps and online resources available that can help you track your food intake and nutrient levels.

- Regular Exercise Routine
While diet plays a significant role in fitness, it’s equally important to establish and maintain a regular exercise routine. Combine cardiovascular exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, with strength training exercises to build muscle and improve overall fitness. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week and incorporate strength training exercises two to three times a week. Consult a fitness professional to design a workout plan that suits your goals and fitness level.

- Seek Professional Guidance
If you’re new to fitness or have specific dietary concerns, consider seeking professional guidance from a registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who specializes in vegetarian or plant-based diets. They can provide personalized advice, help you create a meal plan tailored to your needs, and address any nutritional gaps or concerns you may have.

Conclusion
Achieving fitness with a pure vegetarian diet is entirely feasible with proper planning and attention to nutrient-rich foods. By incorporating plant-based proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, and staying hydrated, you can maintain a well-rounded vegetarian diet that supports your fitness goals. Remember to listen to your body, adapt your diet as needed, and consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance. Embrace the power of a pure vegetarian diet to fuel your fitness journey and promote overall well-being.
REFERENCES:
- Statistical data of Non-communicable diseases (NCDs)-World Health Organization (2022).
- Low and middle-income countries. World Bank Organization.



I’m so in love with this. You did a great job!!
I’m impressed by how sturdy and reliable my ebike is.
I’ve rediscovered my city thanks to my ebike.
This is nicely explained and useful, kudos. I appreciate how you cover key concepts minus hyperbole. It’s useful info and I find you worth following.
This is the type of information I’ve long been trying to find. Thank you for writing this information.
Wow, superb weblog structure! How lengthy have you ever been running a blog for?
you made blogging look easy. The whole look of your site is magnificent, let
alone the content material! You can see similar: dobry sklep and
here sklep internetowy
Wow, this article totally blew my mind! I never knew someone could make vegan cooking sound so exciting. Definitely trying out that quinoa salad recipe!