Food Safety Issues in India: Status, Challenges and Future Prospects
What is Food?
Food is the biochemical entity that carries essential nutrients, minerals, vitamins, and growth regulators that require to run the body’s metabolism. The basic ingredients of the food are carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Consumers want to take good quality food but simultaneously they do not want to compromise their health i.e. the consumers have now become more health-conscious. So this is the time that food processing sectors must focus on food safety along with food quality.
What is food safety?
Food safety in a broader sense can be understood in terms of chemical safety, microbial safety, and physical safety. Among these chemical safety and microbiological safety is the main concern. The chemical safety of food is linked with the contamination of pesticide residues, antibiotics residues, veterinary drug residues, etc. While microbiological safety is concerned with bacteria, viruses, yeast, mold, etc. Food safety outbreaks may take place during the preparation, handling, packaging, and storage of food and food products.
Why Food safety is important?
Globally, millions of people die due to food-borne illnesses which are associated with unsafe food and it may take place due to a lack of sophistication and improper implementation of the HACCP plan during the manufacturing, and processing of food and food products.
Apart from public health, food safety is vital for economic growth and progress as well. In India, the food processing industry holds tremendous opportunities. It has high employment potential, can boost exports of agro-products out of the country, and also provide better returns to farmers for their produce. However, this is possible only if food safety standards are effectively enforced in the country.
The international and national statutory organizations have decided on the permissible maximum residual limits (MRLs) of chemical and microbiological contaminants in the food system. To achieve good safety measures food processing sectors must follow the standards set by statutory organizations. Food should be a source of health, not harm. But food can maim, cripple, and kill. The leading cause of food poisoning is the consumption of contaminated food. Food can become contaminated at any point during production, distribution and processing, or preparation. Everyone along the production chain, from producer to consumer, has a role to play to ensure the food we eat does not cause diseases.
Today, the most concerning food safety issues are the pesticides, insecticides, and other chemical agents in the food system through the practice of conventional farming that ultimately causes severe health problems including kidney diseases, cardiovascular diseases, several types of cancer, etc. The farmers must look at organic farming practices
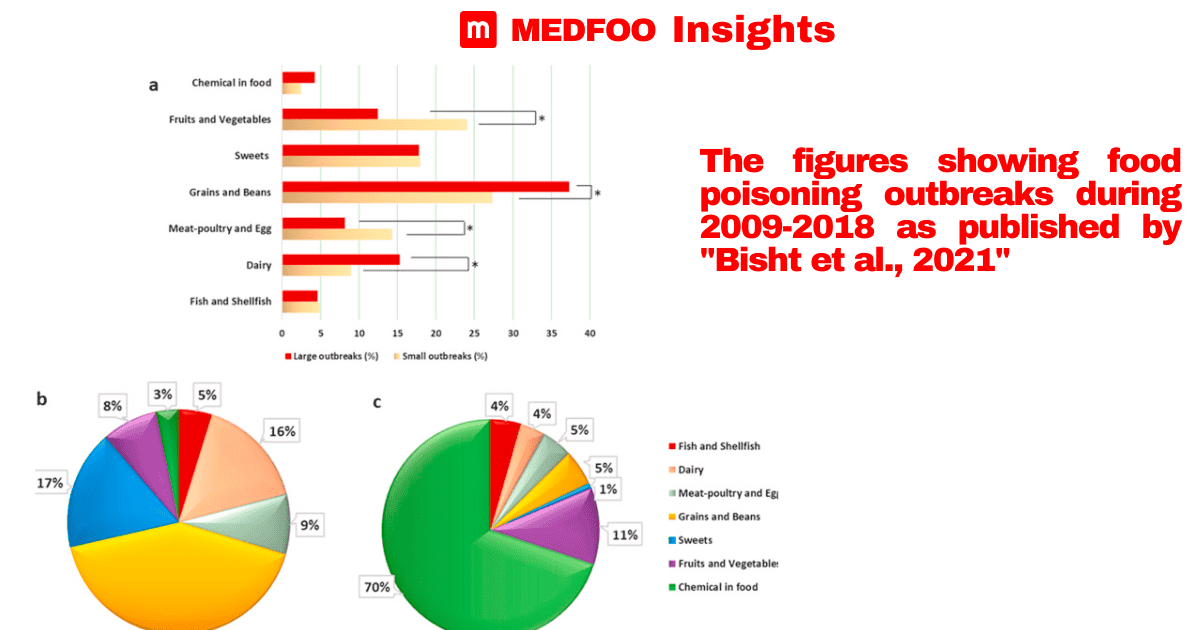
to avoid contamination by such harmful chemical agents. Approximately 16009 cases were detected as per the given sources. Out of the 15163 subjects were hospitalized and the death of 95 subjects took place at last. As per the data, the death rate in the year 2014 was 0.0059%.
To understand the importance of “Food Safety“, let us go through some statistical data on deaths due to food-borne illness worldwide including in India.
Statistical Data on Global Deaths Due to Food-Borne Illness
- As per the World Health Organization (WHO), every year around 600 million cases of foodborne illness take place, of which 420,000 death take place annually.
- Out of total deaths, 30% of death is among children of 5 years of age.
- In a report published by the Journal of medical science, around 2 million (20 lakhs) people die every year due to the consumption of contaminated food and water.
The above information suggests a huge burden of deaths due to foodborne illness. That’s why, It is mandatory to address food safety issues globally. In this article, we will try to sketch out food safety issues in the Indian context.
How to prevent Foodborne illness?
Foodborne illness is completely preventable and World Health Organization smartly plays its role to mitigate the frequency of illnesses caused by infected food and water through its variety of programs running worldwide. In India, the same role is played by FSSAI (Food safety standard authority of India).
Status of Food safety issues in India
India is the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables after China globally. India holds the first rank in buffalo meat production worldwide. The sector of India is one of the strongest agriculture sectors and shares the highest milk production in the world after Denmark. All the above-discussed commodities are perishable commodities that are highly prone to spoilage and deterioration. So, it is needed proper storage and cold chain facility to maintain the food quality and reduce the post-harvest losses that account for the loss of millions of dollars annually in terms of revenue. In India, the Ministry of food processing launched many subsidized schemes regarding the establishment of cold chain infrastructure at the National level.
In India, Industries are divided into two categories i.e.
- Formal Sector: These types of industries are governed by respective government agencies and government has complete data on these industries. such as., Parle-agro Pvt Ltd, Cadbury, Mother Dairy, Amul, Pepsico, etc.
- Informal Sector: These types of industries are governed by government agencies and the government does not have data on these industries. for example., processing units in rural areas, streets, remote areas, etc.
Role of FSSAI in Food Safety Assurance

FSSAI regulates easily the formal sector industries to implement food safety regulations for the assurance of food safety at the end of consumers. In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is the apex food regulator. It is empowered by and functions under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. The FSSAI implements and enforces food regulations as prescribed in the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act). Even the food safety standard authority act-2006 has already been passed in India.
But there is still a need for enforcement in the right way to ensure food safety in the country so that people could live healthier. The country urgently needs a strong infrastructure to enforce the FSSAI-2006 in a better way.
*There are various operations viz.,HACCP, TACCP, and VACCP,which need to be implemented in the food processing industry for food safety assurance.
a. HACCP: Hazard Analysis And Critical Control Points
b. TACCP: Threat Assessment and Critical Control Point
c. VACCP: Vulnerability Assessment and Critical Control Point
The processing units can assure food safety to their consumers by implementing the above operations during food manufacturing, packaging, handling, and storage.





started